The drug, Leqembi, does not reverse symptoms. In patients in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease, it slowed cognitive and functional decline somewhat compared with placebo. The FDA’s approval of Leqembi is not the end of the Alzheimer’s journey, but it could be a way station.
amyloid
Editors at the journal Nature Medicine recently asked researchers and public health experts from around the world to identify clinical trials that will shape medicine in 2023. They came up with a varied list of candidates, from cervical and prostate cancer screening protocols to gene therapy for muscular dystrophy and new drugs for Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. The selections are arbitrary and idiosyncratic, but they are interesting, nevertheless.
A new study shows a strong association between androgen-deprivation therapy for advanced prostate cancer, and the development of Alzheimer's disease. This is a retrospective data-based study, so no change in treatment using ADT is indicated now. Further, prospective studies are needed.
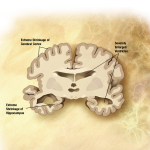
A new study using PET scans on the brains of older individuals shows a three-fold higher risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among those with elevated levels of amyloid-beta, a proteinaceous material associated with neurodegeneration. MCI is a known risk factor for Alzheimer's disease.
Two large meta-analyses in JAMA shed light on the link between Alzheimer s disease and amyloid beta (A-β). The key findings indicate that it is likely to take up to 30 years of amyloid deposition before clear signs of dementia are manifest but such deposits are not diagnostic.
Recently, the FDA has approved new PET tracers as clinical tools to estimate brain amyloid burden in patients being evaluated for cognitive impairment or dementia. And these new tracers - tau-protein tracers - may be
A new study published in Science shows evidence that, in mice, substances like amyloid-beta known to be increased in Alzheimer s disease and others, are removed from the cerebrospinal fluid bathing the brain at an accelerated rate during sleep.