People with red hair tend to have a greater health risk from sun exposure, and for developing skin cancer. But now researchers at Boston University report that they've found a way to potentially reduce that risk by altering a protein involved with pigmentation in humans.
Biomedicine & Biotech
Heparin, which has primarily been used for the treatment of blood clots, is one of the oldest medications still in use. New research indicates that heparin has a more diverse physiological role, one of which stimulates food intake and decreases metabolism. This could have profound clinical implications, both in its current clinical use and for the future of developing weight-loss drugs.
Rapid, accurate detection of a tuberculosis infection still remains a healthcare challenge. Developing an assay that's able to definitively diagnose TB, and one that's cheap, should be high on our priority list. Especially, as we annually see increases in TB's prevalence.
Endorphins, those opiate-type neurotransmitters, are involved in sensations such as "runner's high" — as well as other situations where pleasurable feelings are thought to increase the likelihood that an activity will be repeated. Since eating also increases endorphins, it's been suggested that they might also be responsible for overeating. But a recent study fails to uphold that hypothesis.
Researchers describe wild cattle on Amsterdam Island in the southern Indian Ocean, ones that lost about 25% of their body size in just over 100 years.
Cancer immunotherapy is generating a level of excitement in the medical and scientific community, the likes of which are unprecedented. One scientist's HIV research led him to consider using the HIV virus to kill cancer cells. Cancer immunotherapy could very possibly turn out to be the cure for cancer.
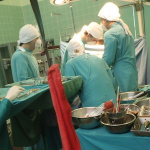
The authors claim that this is the world's first truly successful penis transplant because all functions were restored to normal. They are now recruiting for clinical trials.
Over 1.5 million people have been infected with the Zika virus in the past two years and more than 2,200 babies born with Zika-related microcephaly. Numbers like that call for a clear understanding of how Zika virus is spread from person to person - something that we are still not totally sure about.
Microbiologists have long known that the kitchen is an incredibly fertile field for bacterial growth — and a prime source is the kitchen sponge. A recent study of sponges found that even those that are "cleaned" by their users provide a soup of bacteria — some of which are pathogenic.
A new kind of genetically engineered wheat is more efficient at absorbing phosphorus from the soil and, hence, should require less fertilizer.
It's well known that menopause incurs many negative consequences, including hot flashes, bone loss and added weight in the abdominal area (visceral fat — the worst kind). Any of these can have negative health effects, and current treatment options such as drugs to prevent/treat osteoporosis don't do anything for added fat, or vice versa. But recent research in mice suggests that blocking the hormone FSH could greatly help.
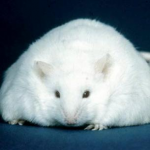
What would you say if there was a way to lose weight while eating a high-fat diet – and you wouldn't even have to sell your soul to the devil? But part of the deal would be that you'd have to stop smelling for a while. Interested? Allow us to explain.