Let’s wax nostalgic. Do you recall the Ebola outbreak a few years ago that brought fear into many American’s lives and ravaged our television screens? Those spacesuit-like outfits medical personnel wore to prevent acquiring the infection were demonstrated by anchors and blasted out via all media forms. The challenge of taking the gear on and off without compromising one’s safety was replayed nearly on a loop.
The messages transmitted then still ring true now regarding the importance of health care worker biohazard protection—not only for themselves, but also the communities they inhabit. In a recent statement put out by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the governing agency revealed the seriousness of their commitment to this preventive measure. We will get to that shortly.
Images of biohazard suits and holding facilities near airports and hospitals were prominently featured a few years ago as was that nurse, Kaci Hickox, who broke quarantine by riding around in Maine on her bicycle while wearing plain clothes. A lot of misreporting and fear abounded especially as the pre-hospitalization route of the Columbia University, Ebola-infected physician was replayed and replayed on television. Not only was the public concern high (and panic tangible) about possible exposure, but the masses were shocked to learn how many places that doctor managed to go in one day in and around Manhattan. To be honest, we all felt a bit lazy in comparison.
No matter how much public health officials explained and insisted or an image like that of former President Obama hugging the Texas nurse recovering from Ebola was presented, it wasn’t until the scare seemed to subside that conventional wisdom was understood. The evidence of minimal United States’ citizens contracting the illness was the reality testing needed. It was then that the concept that health care workers are genuinely at the highest risk compared to the remainder of the public was fully appreciated. And, thus, the tenet of keeping them safe is what keeps the general population safe and suppresses spread was really understood.
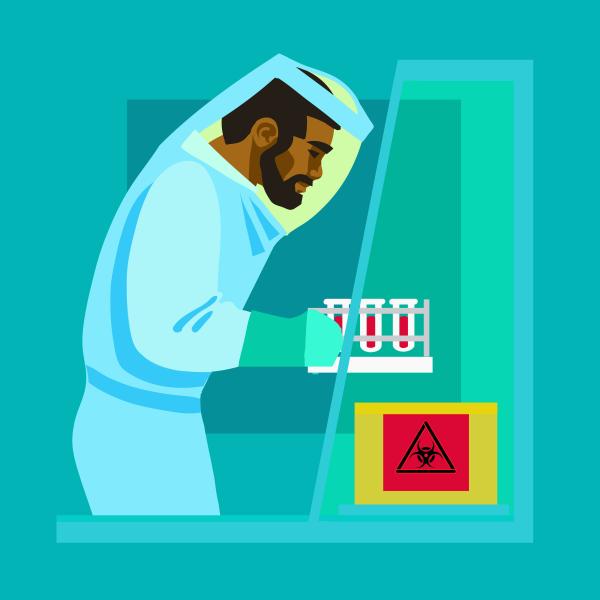
That said, the extreme importance of proper gear was underscored. Hospitals needed to get up to speed in supply to protect their employees as well as all of their patients and families. What most of us don’t realize or think about too often is the fact that scientists and staff who study these major hazards are facing these risks voluntarily each and every day in laboratories to keep all of us safe and progress our society’s treatment and disease management innovations. Their protection is vital to our understanding of contagions.
As a result, the CDC just announced out of an abundance of caution they are temporarily suspending work by lab scientists in BSL-4 (aka biosafety level 4) facilities upon recent discovery their current stock of air hoses attached to the protective suits worn have not been certified for breathing air. They are testing the air that transmits through them for any chemicals that could pose health risks. Air quality tests of current and former employees will be performed since the technology has been in use there since 2005 and they are alerting the safety offices of other labs that might use them as well. There are no known exposures to harmful contaminants or pathogens (which are already HEPA filtered) and the CDC advises the public is not at risk.
Though a temporary inconvenience, assuring the safety and well-being of these—often called— disease cowboys is in our best interest. They are the greatest threat to present and future microbes and outbreaks!
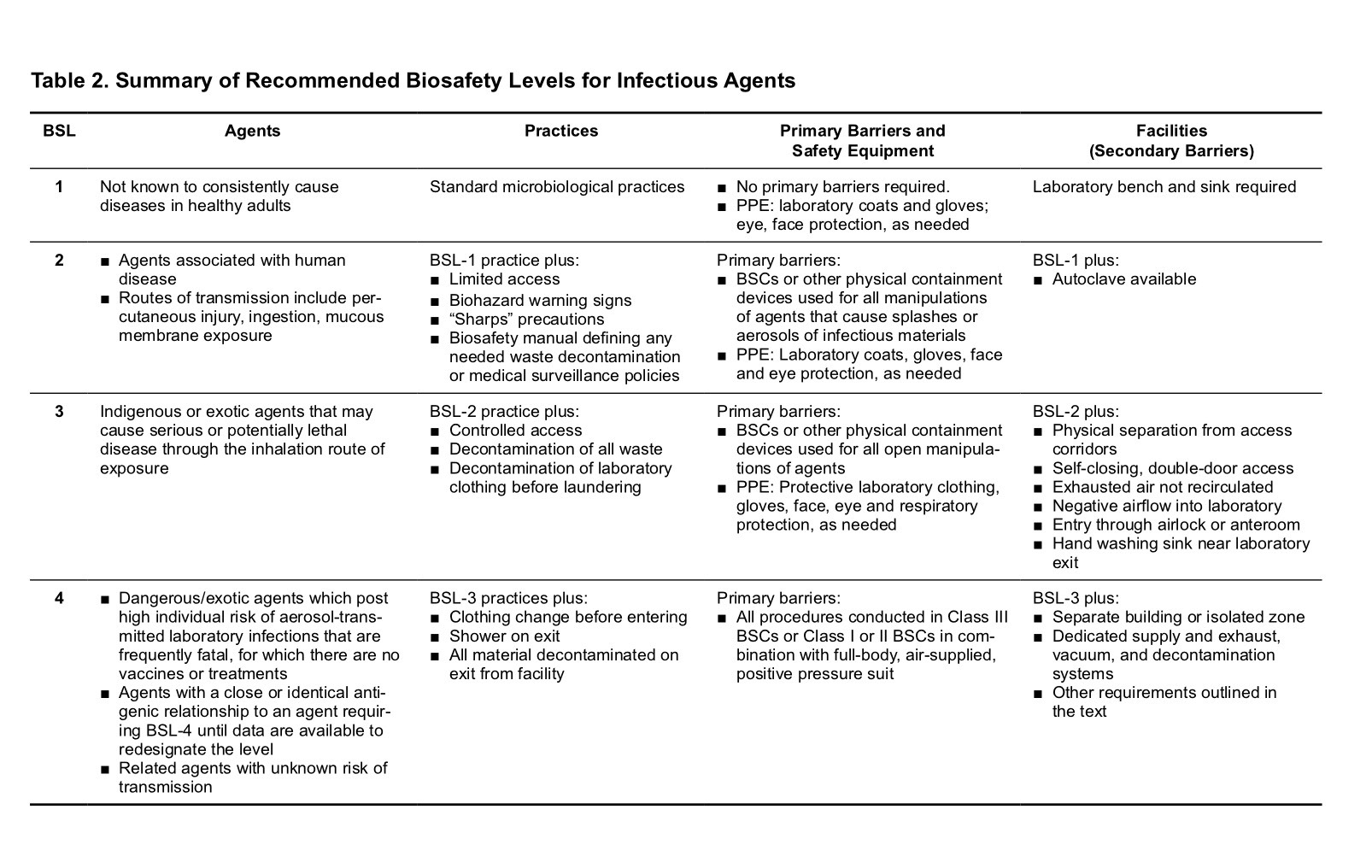
What do the biosafety levels of these labs mean?
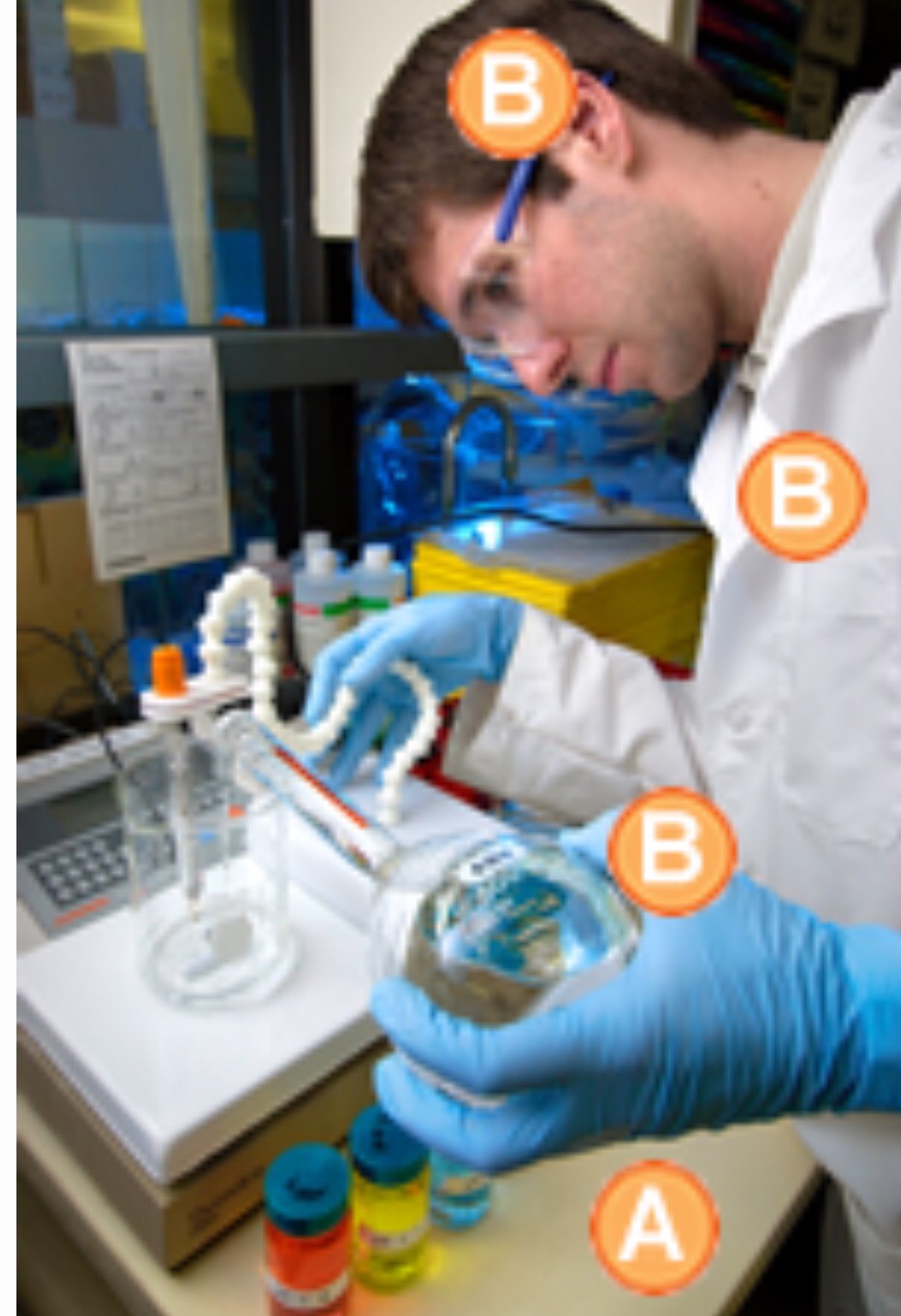
Labs are identified by lowest microbe risk BSL-1 to highest risk BSL-4. BSL-1 entails personal protective equipment (PPE) of lab coat, gloves and eye protection with standard safety protocols (e.g. a close by sink for hand washing, doors to partition the lab from external surroundings). The bugs (e.g. nonpathogenic strain of E. Coli) worked with pose a minimal risk of causing disease in otherwise healthy adults. BSL-2 PPE adds to BSL-1 with face shields, performing procedures in a safety cabinet to avoid infection by splashes, self-closing doors, and use of a superior modes to decontaminate instruments. This is for strains that have moderate risk causing disease (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus). BSL-3 adding to BSL-2 with coverage against more exotic etiologies that yield bad to potentially lethal disease acquired by inhalation routes (aka respiratory transmission for bugs like Mycobacterium tuberculosis). These settings are restricted access (e.g. two sets of doors) and the employees receive vaccinations and medical observation. They must wear respirators and air entry is controlled nonstop- as is the entire place. BSL-4 is all of the aforementioned and then some since pathogens with capacity for airborne spread and deadly disease are a mainstay of this level. These bugs have no cures (e.g. Ebola, Marburg). The PPE includes a full body suit with its own air supply. It is a remote complex typically and requires substantial decontamination measures upon exiting. (1)
What does PPE look like? (2)
BSL-1 BSL-4
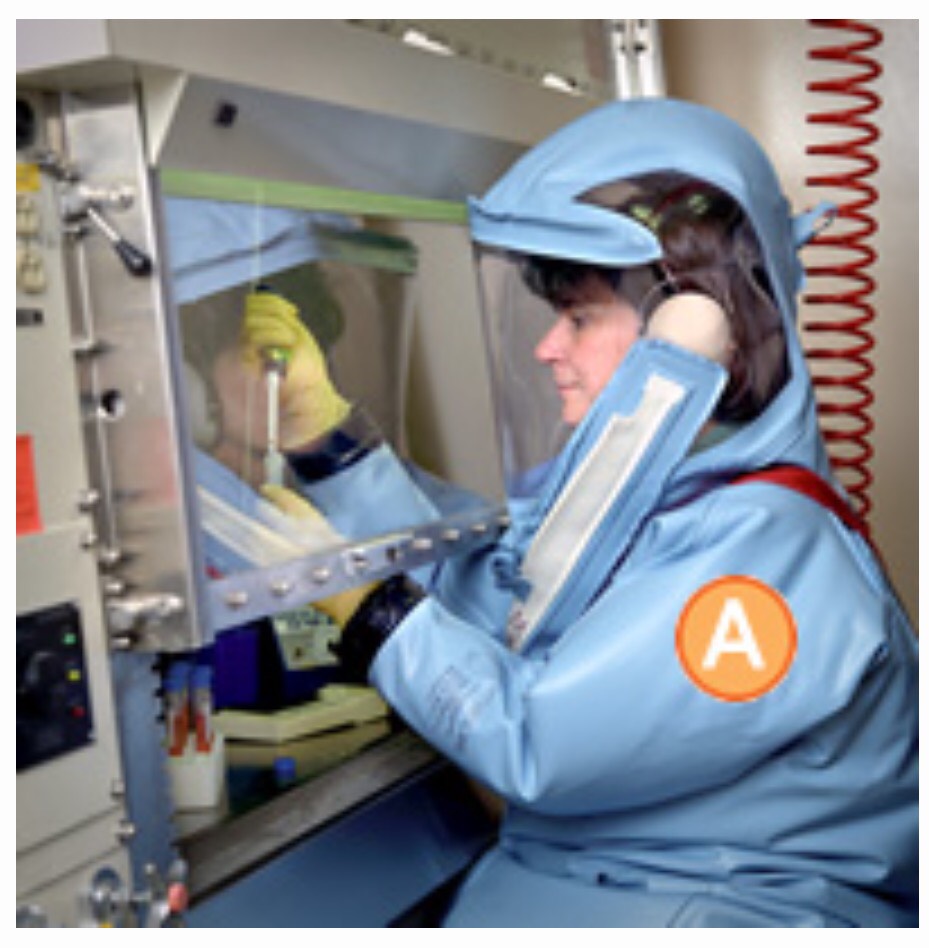
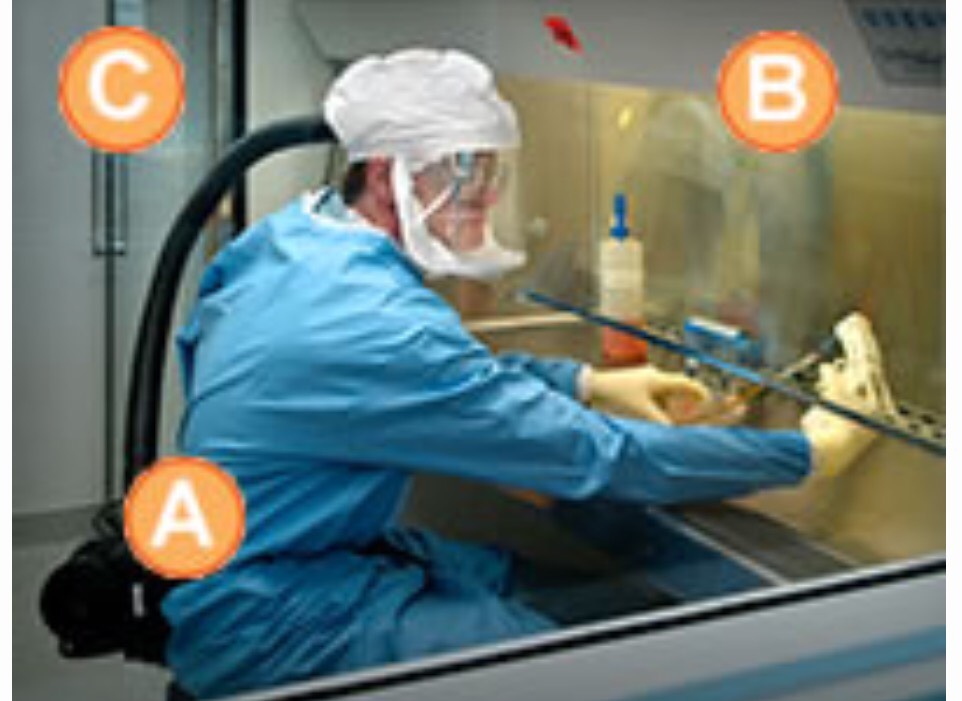
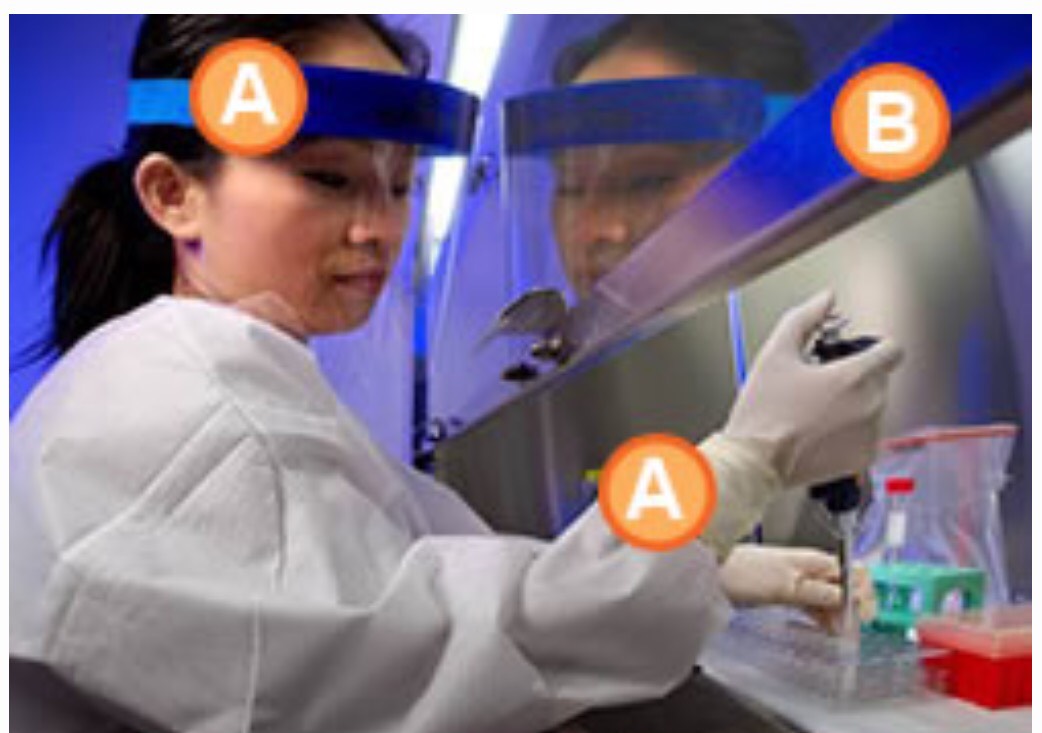




BSL-3 BSL-2
SOURCE(S):
(1) (2) This paragraph (and above photos) summarizing the BSL levels was condensed from this very informative Quick Learn Lesson published here by the CDC. The more extensive rule book for these laboratories by the CDC (from where the above table was procured) is available by clicking here and here.




