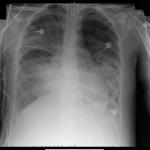
Throughout the month of January, the world was gripped by an unfolding drama. Glued to their television sets and social media accounts, people were sharing news stories and punditry, eager to learn of the latest developments.
Disease
By Alex Berezow, PhD; Josh Bloom, PhD; Chuck Dinerstein, MD, MBA; and Thom Golab
The conventional wisdom regarding COVID-19 changes every other week.
Mayor Giuliani now thinks he's Dr. Giuliani. His website is offering up two very bad videos on coronavirus and COVID-19.
My generation, the Boomers, are not shy in expressing their opinions, but what about those of us, slightly older, the generation of the Korean war, so “inconsequential” that their name is “The Silent Generation,” lost between the Greatest Gene
There's something irresistible about conspiracy theories.
Oxygen moves in and out of our bloodstream by the passive process of diffusion – higher amounts moving towards lesser amounts in an attempt to equalize.
We have gotten used to trolls and political ideologues spreading misinformation about public health. But it's still a surprise when alleged science journalists do it.
Masks are two-way filters between the environment and your airway; they are a compromise between their ability to filter out particles and your ability to breathe.
Before we jump in, there is one caveat, the medical data surrounding Covid-19, is in flux because we lack standardization of information globally.