In spite of study after study and the writings of expert after expert over the last 25 years, we, as a society, have failed to provide for our own security in the face of a potential public health threat. We have failed to supply and ma
Drugs & Pharmaceuticals
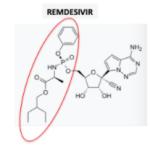
It is rare to find a mention of Giliead's remdesivir, arguably the most promising drug in the fight against coronavirus, without also hearing that it failed miserably in fighting Ebola.
Press briefings, by any measure, are long and loud. And now they may get longer and louder since there is another potential antiviral drug to yell about.
I thought that this would be a good time to review the various vaccines and therapies being studied to combat the coronavirus pandemic.
By Katherine Seley-Radtke, University of Maryland, B
In the next few weeks, we will experience the downside risks of offshoring. Moving manufacturing to areas with specialized expertise should reduce costs and provide a better product.
On March 23 Arizona Governor Doug Ducey sent a letter to Seema Verma, Administrator of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, informing
Within the coming weeks, we should be starting to get a picture of whether remdesivir will be a savior to the world, just another failed drug, or something in between.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that cause disease in animals and humans.
Two drugs, chloroquine (CQ), and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) are all over the news because both drugs are being extensively studied for their antiviral potential against coronavirus.